. A device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another circuit.
. Used to step up and step down AC voltages.
. Uses principle of mutual induction.
. Mutual Induction: Production of electromotive force in circuit by current changing in second circuit which is linked magnetically to the first.
. William Stanley built the first commercial transformer in 1886.
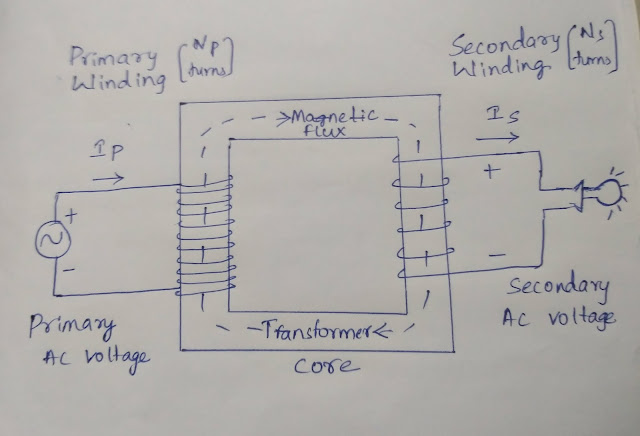
Construction:
. Input connections: Input source is connected - Primary side.
. Output connections: Transformed power is sent to load - Secondary Side.
. Windings: Primary- draws power from source.
Secondary- delivers transformed voltage to load.
. Core: Provides controlled path for magnetic flux generated.
Working:
. Primary coil is connected to AC supply.
. An alternating current passes through primary coil wrapped around soft iron core.
. Changing current produces changing magnetic filed.
. This induces alternating voltage in secondary coil.
. This induces AC in circuit connected to secondary coil.
Note:
. No electric connection between primary and secondary.
. Only AC is supplied to primary.
. If DC is supplied, no current is induced in secondary.
Types of Transformers:
Based on Voltage levels:
1. Step-Up Transformer: Secondary voltage is stepped up by increasing number of windings in secondary coil.
2. Step-Down Transformer: Secondary voltage is stepped down by decreasing number of windings in primary coil.
Based on Core:
1. Core: Winding surrounds laminated core.
2. Shell: Laminated core surrounds Winding.
Based on Winding:
1. Standard: Primary and Secondary winding placed in different regions.
2. Auto Transformer: Windings connected to each other in series.
Based on Usage:
1. Power Transformer: Bigger in size.
Suitable for high voltage power transfer.
Used in power generation stations and transmission substation.
2. Distribution Transformer: Smaller in size.
Works with 50-70% efficiency.
Used to distribute power generated from plant to remote locations.
3. Measurement Transformer: Used to measure electrical quantity like voltage, current, power.
4. Protection Transformer: Used in component protection purpose.
Usage of Transformers:
. Used everywhere like from home appliances to large systems.
. Adapters and chargers of mobile phones.